Basic Info.
Final Product Usage
Make Charcoal Briquettes
Color
Customer′s Request
Carbonization Time
8-30hour
Instalation
Engineer Guide
Origin
China
Product Description
Products Description

Biochar (English: Biochar) is a kind of charcoal used as a soil conditioner, which can help plants grow, and can be used for
agricultural purposes and carbon collection and storage, which is different from traditional charcoal generally used for fuel.
Like ordinary charcoal, biochar is the product of biomass energy raw materials after pyrolysis, and its main component is carbon molecules. Because of the study of the black soil of the Amazon, scientists became interested in biochar. In Japan, the use of biochar in agriculture also has a long history.
In recent years, due to the impact of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane on climate change, scientists have begun to pay attention to the use of biochar, because it helps to capture and remove greenhouse gases in the atmosphere through biochar sequestration. Convert it to a very stable form and store it in the soil for thousands of years.
In addition, using biochar can increase agricultural productivity by 20%, purify water quality, and help reduce the use of
chemical fertilizers.
agricultural purposes and carbon collection and storage, which is different from traditional charcoal generally used for fuel.
Like ordinary charcoal, biochar is the product of biomass energy raw materials after pyrolysis, and its main component is carbon molecules. Because of the study of the black soil of the Amazon, scientists became interested in biochar. In Japan, the use of biochar in agriculture also has a long history.
In recent years, due to the impact of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane on climate change, scientists have begun to pay attention to the use of biochar, because it helps to capture and remove greenhouse gases in the atmosphere through biochar sequestration. Convert it to a very stable form and store it in the soil for thousands of years.
In addition, using biochar can increase agricultural productivity by 20%, purify water quality, and help reduce the use of
chemical fertilizers.
Technical Parameters
| Equipment model classification | THJ-1 | LXTHJ-2 | LXTHJ-3 |
| Pipe diameter (mm) | Ø800*1200 | Ø1000*1600 | Ø1200*2000 |
| Equipment output (kg/h) | 400-500 | 600-800 | 800-1000 |
| Fan power (kw) frequency conversion speed regulation | 7.5 | 11 | 15 |
| Continuous carbonization machine main engine power (kw) speed regulation | 4 | 5.5 | 7.5 |
| Cooling charcoal machine motor power (kw) | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Screw feeder motor power (kw) | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Burner(s) | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Liquefied gas burner (pcs) | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Auxiliary burner (pcs) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Working temperature of high temperature carbonization pipeline (ºC) | 500-800 | 500-800 | 500-800 |
| Furnace temperature (ºC) | 350-800 | 350-800 | 350-800 |
Ways to turn waste into treasure
Many other materials can also be used to make charcoal, such as a large amount of animal and plant waste from agriculture-wheat straw, seed husks, manure, etc.; human-made waste-such as sewage sludge or other domestic waste can come in handy. The use of waste to produce biochar also has a double carbon reduction effect. If manure is left to rot, it can produce methane. Methane is also a greenhouse gas, and its impact on the greenhouse effect is more than twenty times that of carbon dioxide.
Many other materials can also be used to make charcoal, such as a large amount of animal and plant waste from agriculture-wheat straw, seed husks, manure, etc.; human-made waste-such as sewage sludge or other domestic waste can come in handy. The use of waste to produce biochar also has a double carbon reduction effect. If manure is left to rot, it can produce methane. Methane is also a greenhouse gas, and its impact on the greenhouse effect is more than twenty times that of carbon dioxide.

Product Application
Raw materials
seeds;
shells and pits of tree-fruits;
wood chips;
bamboo;
shrubby and other plant materials, the fraction of which is from 5 to 30 mm with a moisture content of not more than 15%.
shells and pits of tree-fruits;
wood chips;
bamboo;
shrubby and other plant materials, the fraction of which is from 5 to 30 mm with a moisture content of not more than 15%.

| Coconut shell | Walnut shell | Hazelnut shell | Wood chips | Bamboo |

| Coconut shell charcoal | Shell charcoal walnut | Hazelnut shell charcoal | Wood chips charcoal | Bamboo charcoal |

| Palm kernel shell | Pits of olives | Pits of date | Peach Shell | Hawthorn Seed |

| Palm kernel charcoal | Pits of olives charcoal | Pits of date charcoal | Peach Shell charcoal | Hawthorn Seed charcoal |
Received products
Raw materials for obtaining activated carbon Raw Material for BBQ Charcoal Briquette and Industry Raw materials for the production of coal briquettes for hookahs (hookah, hookah coal)
BIO-Char, as a fertilizer or hydroponic growth intended for the agricultural industry, is made from plant raw materials and does not contain harmful substances.

Working principle and process
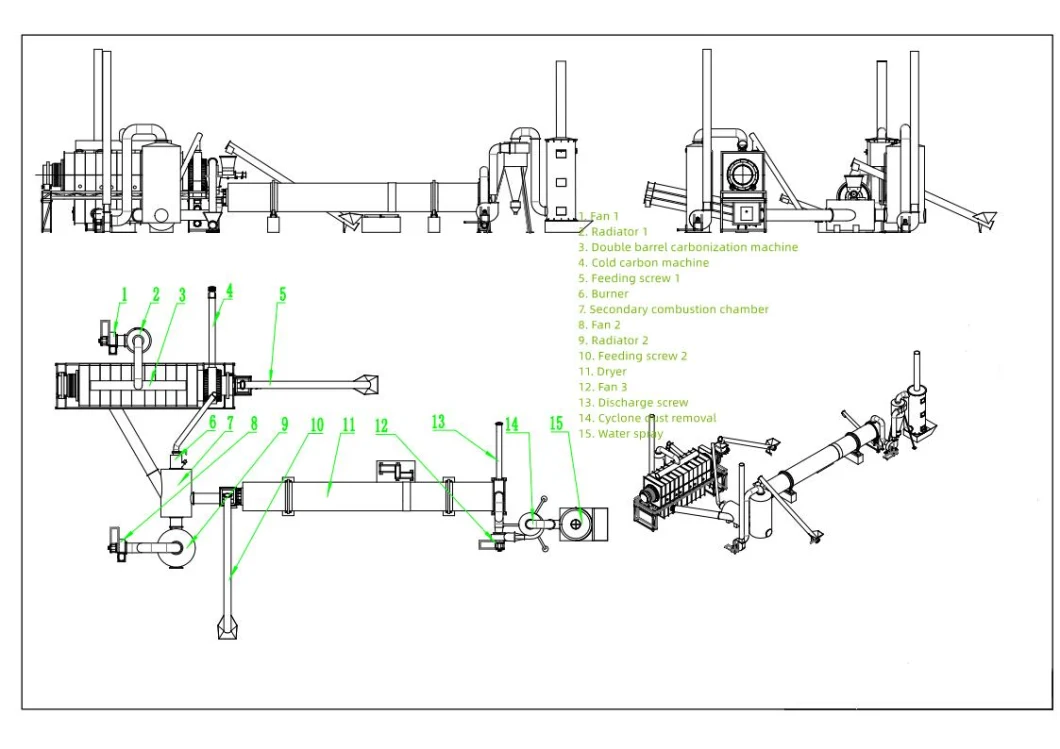
Brief description of the production process
Pyrolysis manufacturing
People have used charcoal as fuel for thousands of years, and its manufacture is simple: burn wood, straw or crop waste in an oxygen-deficient environment, and the resulting substance is charcoal. The traditional method is to cover the ignited biomass with earth and let it burn flamelessly for a long time.
Pyrolysis to make biochar
Large-scale industrial production of charcoal by traditional methods is impractical. Researchers have set their sights on the "pyrolysis" method - at high temperatures of 500°C to 600°C, placing organic substances in an oxygen-deprived state for controlled pyrolysis. In addition to yielding charcoal, pyrolysis can produce by-products such as syngas and liquid tar, both of which can be used as fuel for power generation or heating. The yield of biochar depends on the speed of the pyrolysis process. Rapid pyrolysis can yield 20% biochar, 20% syngas and 60% bio-oil. And slow pyrolysis can produce 50% charcoal and a small amount of oil. The British Institute for Management and Sustainable Development believes that because modern pyrolysis plants can run entirely on syngas, the energy produced is three to nine times the energy cost required.
People have used charcoal as fuel for thousands of years, and its manufacture is simple: burn wood, straw or crop waste in an oxygen-deficient environment, and the resulting substance is charcoal. The traditional method is to cover the ignited biomass with earth and let it burn flamelessly for a long time.
Pyrolysis to make biochar
Large-scale industrial production of charcoal by traditional methods is impractical. Researchers have set their sights on the "pyrolysis" method - at high temperatures of 500°C to 600°C, placing organic substances in an oxygen-deprived state for controlled pyrolysis. In addition to yielding charcoal, pyrolysis can produce by-products such as syngas and liquid tar, both of which can be used as fuel for power generation or heating. The yield of biochar depends on the speed of the pyrolysis process. Rapid pyrolysis can yield 20% biochar, 20% syngas and 60% bio-oil. And slow pyrolysis can produce 50% charcoal and a small amount of oil. The British Institute for Management and Sustainable Development believes that because modern pyrolysis plants can run entirely on syngas, the energy produced is three to nine times the energy cost required.


Product packaging

Company Profile
Baoyuan Machinery is a comprehensive enterprise that comprises R& D, test, manufacture, sales and service functions. We have succeeded in researching and supplying solutions with the following equipment: Drying equipment, activated carbon production equipment, building materials equipment, beneficiation equipment, crushing equipment and other products.
With our leading-edge technologies, advanced processing equipment and our corporate spirit of "innovation, pragmatism, unity, hard work and dedication", our company has the strength to meet the challenges from all aspects. We have the confidence to build "Baoyuan" into a world-renowned brand, provide quality services for the dryer and building processing industry, and achieve a win-win situation between the company and customers.

